Did you Make Over $125,000 Individually or over $200,000 as a Married Couple?
There are two new local personal income taxes that became effective for the 2021 tax year. These two taxes, explained below, are specifically for single filers with Oregon taxable income above $125,000 and married jointly filers with Oregon taxable income above $200,000.
These two programs are local taxes, not state taxes. This means that the tax payments go directly to The City of Portland and require an additional filing. We expect high-income earners in the Portland-metro area to have at least three tax returns for 2021: US Individual Income Tax Return, Oregon Income Tax Return and City of Portland.
Like your federal and Oregon state tax return, these local tax returns are also due by Monday, April 18.
Local tax #1: Preschool for All (PFA) Personal Income Tax
In November 2020 Multnomah County voters passed The Preschool For All Program which will provide tuition-free preschool for children that meet the program criteria.
This local tax is funded by a 1.5% marginal personal income tax on taxable income above $125,000 for single filers and $200,000 for those married filing jointly.
This local tax is also funded by an additional 1.5% tax is imposed on taxable income over $250,000 for single filers and $400,000 for those married filing jointly
Local tax #2: Portland Metro Tax
In May 2020, Portland-area voters approved Measure 26-210 which will provide homelessness services like shelter, advocacy, and mental health resources.
This local tax is funded by a 1% marginal personal income tax on taxable income above $125,000 for individuals and $200,000 for those married filing jointly.
This local tax is also funded by a 1% business income tax on net income for businesses with gross receipts above $5 million.
The Portland Metro area includes residents of Multnomah County, Clackamas County, and Washington County. For a full reference guide of the Metro jurisdiction use this online tool.
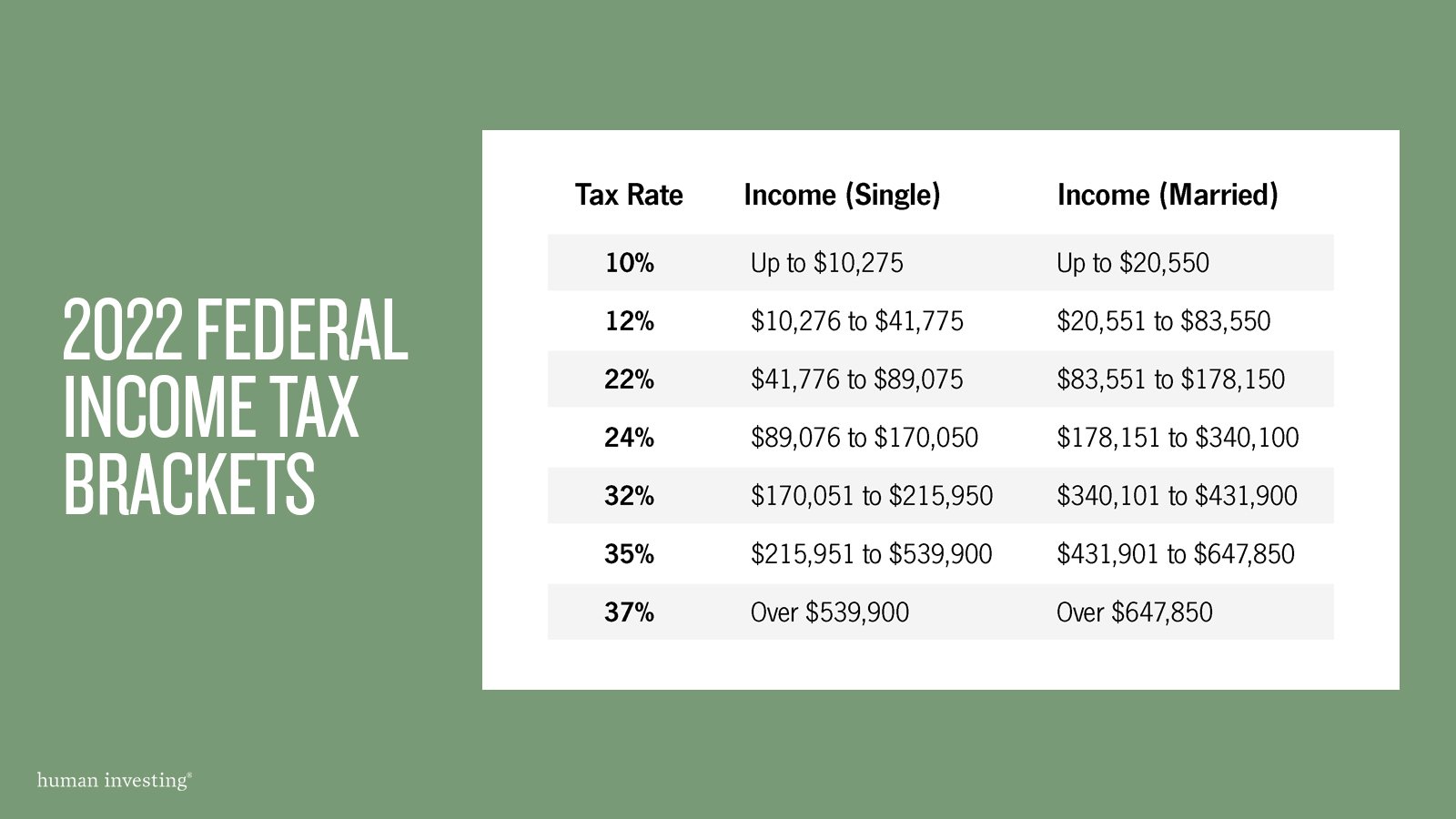
How can I Find my 2021 Taxable Income?
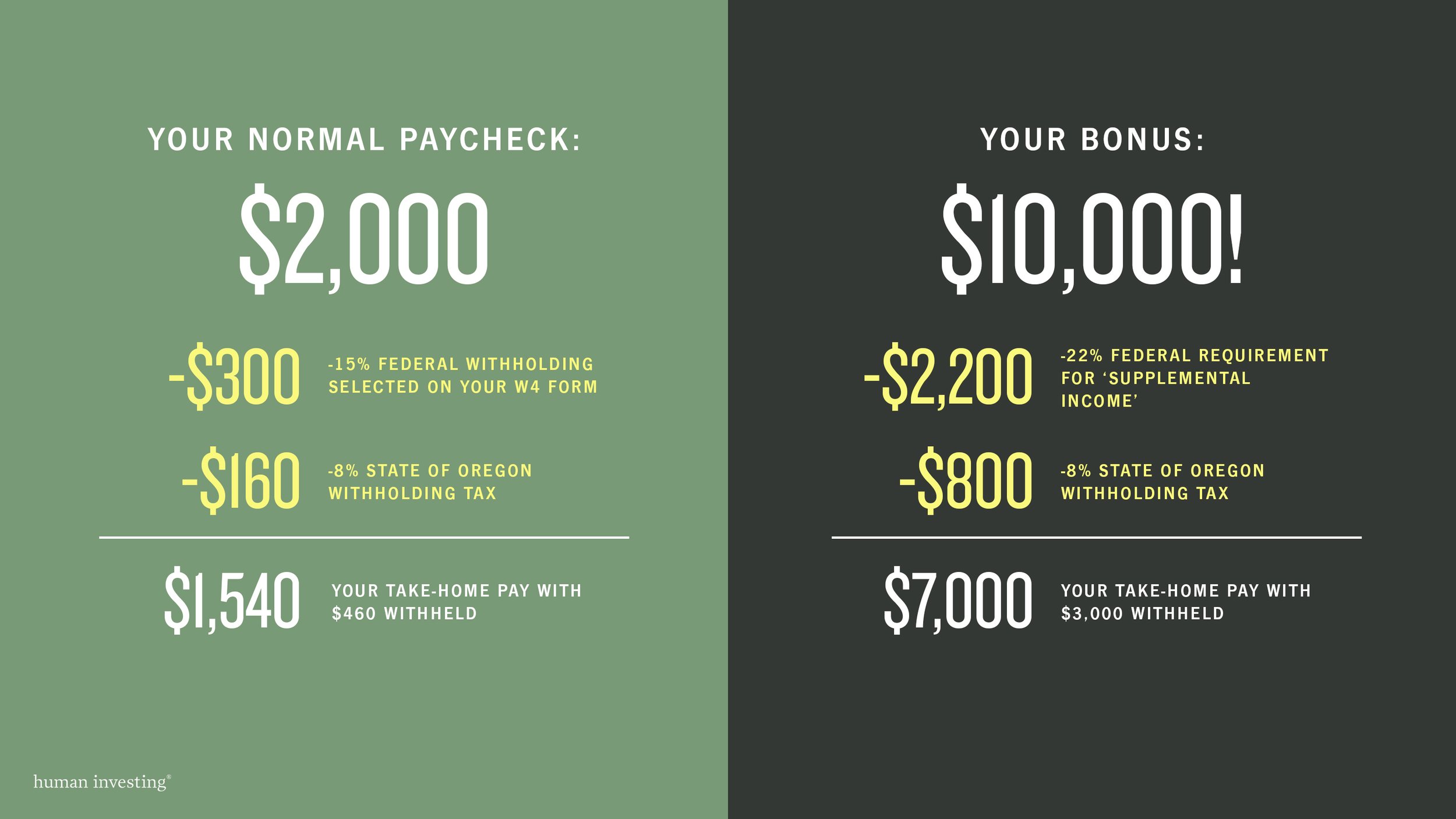
Taxes are complicated. Remember that your income (like your salary) is not the same as your taxable income. For example, you could earn a salary of $140,000 a year but have less than $140,000 of taxable income because of pre-tax retirement account contributions and taking the standard deduction or itemized deductions.
The easiest way to confirm your 2021 Oregon taxable income is to complete an Oregon Income Tax Return. Your taxable income is included on line 19 of your Form Oregon 1040.
If you are a single filer and your Oregon taxable income (on Line 19 on your 2021 Form OR-40) is greater than $125,000 or if you are a married jointly filer and your Oregon taxable income is greater than $200,000 then you likely need to pay your taxes by April 18, 2021.
FINDING YOUR TAXABLE INCOME IN TURBOTAX
1. Login and find the Documents tab.
2. Download your tax PDF. Scroll to the bottom of the PDF for the Oregon return.
3. Find your 2021 Form OR-40. Line 19 includes your total taxable income.
examples of Calculating your local taxes owed
Preschool For All Tax: $0 because her income is below the $125,000 threshold for individual taxpayers.
Portland Metro Tax: $0 because her income is below the $125,000 threshold for individual taxpayers.
Preschool For All Tax: $6,000.
Tier 1: $400,000 - $200,000 = $200,000 of taxable income. $200,000 x 1.5% = $3,000
Tier 2: Then, $500,000 - $400,000 = $100,000 of additional taxable income. $100,000 x 3% = $3,000
Portland Metro Tax: $3,000.
$500,000 - $200,000 = $300,000 of taxable income. $300,000 x 1% = $3,000
Preschool for All Tax: $0 because they are not a Multnomah County resident.
Portland Metro Tax: $350.
$160,000 - $125,000 = $35,000 of taxable income above the threshold. $35,000 x 1% = $350
How Can I Pay for this Tax?
If you hire a CPA to prepare your individual tax returns, we recommend confirming that they will also file your City of Portland taxes for you.
If you use an online tax software like turbotax, you will have to visit the Pro.Portland.gov website to submit your tax payments in a separate return. If you are a Multnomah County resident, this process will feel similar to paying your $35 Arts Tax.
What if my Taxable Income is Below the Limits for the PFA and Metro Tax?
You do not need to file anything to the city of Portland if your taxable income is below the limits for both local taxes in 2021. However, if you are a Multnomah County resident then don’t forget to pay your Multnomah County Art Tax for 2021. You can pay for it here: Portland Arts Tax Online Payment.
If you have more questions about the new local taxes, or would like to speak to a financial professional please reach out to us at hi@humaninvesting.com or 503-905-3100.